Breast Reconstruction Surgery: Improving Quality of Life After Breast Cancer

According to data released by the WHO in 2023, approximately 2.3 million women worldwide were diagnosed with breast cancer in 2020, and about 685,000 died from the disease. Furthermore, at the end of 2020, an estimated 7.8 million women who had been diagnosed with breast cancer in the previous five years were still alive.
With so many women experiencing breast cancer, treatment focuses not only on removing the cancer itself, but also on the patient's physical and psychological recovery after surgery. Today, we will explore breast reconstruction surgery in detail, a crucial consideration for improving the quality of life for patients after breast cancer surgery.
Mastectomy can lead to significant changes in appearance, and these sudden changes can cause mental shock, feelings of loss, and depression. Many breast cancer patients experience deep sadness and decreased self-esteem due to the loss of femininity after surgery, which can negatively impact their daily lives and interpersonal relationships.
Moreover, the weight difference between the breasts can lead to postural imbalances, causing chronic shoulder or neck pain, which can burden the entire musculoskeletal system in the long term. Therefore, breast reconstruction surgery is not just a matter of cosmetic or psychological concern; it is essential for daily life and activities.
For these reasons, Korea has included breast reconstruction surgery in its national health insurance coverage for patients who have undergone total mastectomy (removal of the entire breast) since 2015, providing support for many breast cancer patients to receive breast reconstruction surgery.
Methods of Breast Reconstruction Surgery
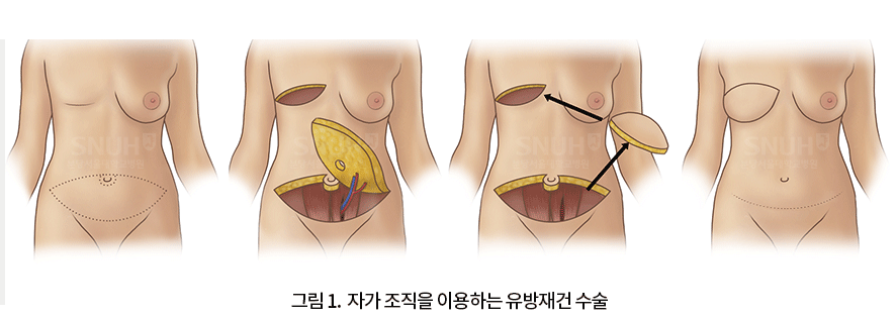
There are two main methods of breast reconstruction surgery: using autologous tissue and using breast implants. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, so it is important to determine the most appropriate surgical method for each individual. Various factors must be comprehensively considered, including the patient's age, body shape, health condition, surgical method, breast cancer treatment plan other than surgery, and individual preferences.
For example, autologous tissue reconstruction may be more suitable if a significant amount of breast skin has been removed, if there is sufficient abdominal fat, or if radiation therapy is planned. On the other hand, implant reconstruction may be a better choice if most of the breast skin is preserved, if rapid recovery is desired, or for those with a slender body type who do not want additional scars.
The timing of surgery can also be chosen between immediate reconstruction, which is performed simultaneously with breast cancer removal surgery, and delayed reconstruction, which is performed after a certain period. This allows for a customized treatment plan tailored to each patient's situation.
The first method, breast reconstruction using autologous tissue, involves transplanting fat from the abdomen or back to the chest area. If there is sufficient abdominal fat, a sufficient volume of tissue can be transferred, and a softer, more natural breast shape can be expected.
There is also the added benefit of a tummy tuck effect, and the tissue transferred to the chest is more resistant to radiation therapy. Breast reconstruction surgery using this abdominal flap technique is known to be a safe and effective procedure.
However, this method has the disadvantage of leaving a long horizontal scar along the underwear line on the lower abdomen, requiring a lengthy surgery time of at least 4-5 hours, a high level of surgical difficulty, and, rarely, complications such as abdominal wall weakness or hernia in the abdomen where the tissue was harvested.
Back fat can also be used as autologous tissue. Although the final scar is shorter and the surgery time is less than half that of abdominal fat, the volume of tissue that can be transferred is smaller. Therefore, it can be chosen when a partial mastectomy is performed or when a relatively small amount of tissue is needed after a total mastectomy.
The second method involves inserting a breast implant into the chest area. This method applies breast implants, which have been widely used in cosmetic breast augmentation surgery, to breast reconstruction surgery.
This is the preferred method when the breast skin is almost entirely preserved during mastectomy, and only the volume inside needs to be filled without the need to reconstruct the skin. It can also be chosen when there is not enough abdominal or back fat to use autologous tissue.
Reconstruction surgery using implants usually takes about an hour, is relatively simple, and has the advantage of not leaving scars on other parts of the body. However, complications related to breast implants can occur, and breast implants have a limited lifespan, so follow-up observation is necessary.
When a breast implant is placed in the body, a capsule forms around the implant. If the capsule becomes thickened or excessively contracted, capsular contracture can occur, causing the breast to become hard or change shape. In very rare cases, specific diseases have been reported, so if symptoms such as changes in breast shape, pain, or hard lumps appear, a medical examination should be performed.
Complications of Breast Reconstruction Surgery
Both surgical methods are continuously being researched to improve the completeness of the results and minimize the occurrence of complications.
In particular, microsurgical techniques using autologous tissue have recently become highly sophisticated, and research is actively being conducted to reduce complications that may occur in the abdominal area after abdominal fat transfer.
In 2021, a research team led by Professors Myung Yu-jin, Chung Jae-hoon, and Huh Chan-young of the Department of Plastic Surgery at Seoul National University Bundang Hospital conducted a study analyzing the incidence and risk factors of complications after breast reconstruction surgery using abdominal flaps.
The research team analyzed a total of 13 items using machine learning, including kidney function, weight, age, medical history, amount of abdominal wall fascia harvested during surgery, type of breast cancer removal surgery, and whether or not chemotherapy or radiation therapy was performed after surgery, based on data from 568 patients (average age 48.7 years) who underwent breast reconstruction surgery with abdominal flaps at Seoul National University Bundang Hospital from 2006 to 2019.
The results showed that the incidence of postoperative complications varied from 1.7% to as high as 26% depending on the patient's individual risk. In particular, patients were classified as high-risk if the area of abdominal flap tissue harvested during surgery was 37.5cm2 or more, and low-risk if it was less than that. Individual underlying diseases were also identified as factors that increased the risk of complications.
Meanwhile, efforts are continuing to minimize capsular contracture and lymphoma development in reconstruction surgery using breast implants. Recently, smooth-surfaced implants with a very low risk of lymphoma development have been used, and acellular dermal matrix (ADM) is applied together to minimize the possibility of complications by preventing the implant from directly contacting body tissues.
The same breast reconstruction surgery method cannot be performed on all patients. A customized surgery must be selected according to the individual's body, the method of resection surgery, and the desired goals. The role of the plastic surgeon is very important at this time, and they must fully explain the advantages and disadvantages of each surgery and how these advantages and disadvantages will affect the individual patient.
Breast reconstruction surgery can be performed regardless of the timing, and the most appropriate surgical method can be selected depending on the extent of the mastectomy and the patient's physical condition. Both autologous tissue and breast implant methods are constantly being researched to proceed as safely as possible, so you don't have to worry too much if the surgery is performed after sufficient consultation with surgical and plastic surgery medical staff.
More Useful Information from Seoul National University Bundang Hospital
Go to Other Posts









Source :https://blog.naver.com/happy_snubh/224060274224
No comments yet.
