Understanding Breast Cancer: Types, Risk Factors, and Treatment Option…
페이지 정보
작성자 Wassup 작성일 25-11-12 22:45 조회 24 댓글 0본문
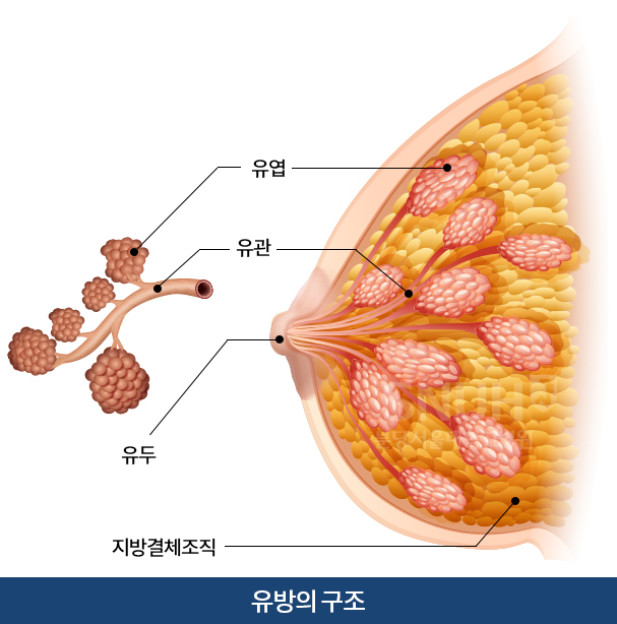
A normal breast consists of glandular tissue and the surrounding fat, connective tissue, and lymphatic vessels that support it. The glandular tissue is composed of lobules that produce milk and ducts that connect the lobules to the nipple. Breast cancer can originate in any of these tissues, making it a diverse disease compared to other cancers.
Most breast cancers begin in the cells of the ducts and lobules. Therefore, the term 'breast cancer' often refers to cancer that arises from the epithelial cells of the ducts and lobules.
Estrogen, a crucial hormone for maintaining female characteristics, can also stimulate the proliferation of duct cells. Prolonged exposure to this hormone may increase the risk of breast cancer.
This risk applies to estrogen from oral contraceptives and post-menopausal hormone therapy, as well as the estrogen produced during normal menstrual cycles. Some reports suggest that oral contraceptives can double the risk of breast cancer. However, low-dose oral contraceptives used by young women are considered to pose minimal risk.
Nonetheless, indiscriminate use of hormone therapies should be avoided. If undergoing hormone therapy, annual check-ups for endometrial and breast cancer are recommended.
Most breast cancers are detected after the age of 40, and the incidence increases with age. Women who have few or no children, have their first child later in life, or do not breastfeed are at higher risk. Obesity, especially after menopause, is also a significant risk factor. Other risk factors include radiation exposure, a high-fat diet, alcohol consumption, and environmental hormones.
In 5-10% of breast cancer patients, genetic factors, specifically genes involved in breast cancer development, play a role. Mutations in genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2 are common examples, and can lead to breast cancer at a younger age. Family history, separate from genetic inheritance, can also elevate breast cancer risk. Individuals with a mother or sister who has had breast cancer have a 2-3 times higher risk compared to those without such a family history. If both mother and sister have had breast cancer, the risk increases by approximately 8-12 times.
However, family history accounts for only 10-15% of breast cancer cases, so the risk should not be ignored simply because there is no family history.
Surgery is the most definitive treatment for breast cancer, with two main types: total mastectomy and partial mastectomy (breast-conserving surgery). A total mastectomy involves removing the entire breast, including the nipple and skin, while a partial mastectomy involves removing only the tumor and some surrounding tissue, preserving the breast.
The use of partial mastectomies has gradually increased as their therapeutic effectiveness and safety have been established. Currently, about two-thirds of patients undergo partial mastectomies.
Since the breast is a symbol of femininity, minimizing the sense of loss while treating the cancer is important. If a total mastectomy is unavoidable, immediate breast reconstruction surgery is recommended. Delayed reconstruction surgery is also increasingly recommended for patients who have already undergone a total mastectomy.
Recently, even with total mastectomies, it has become possible to preserve the skin and nipple while removing only the breast tissue, and to perform immediate reconstruction surgery to preserve the breast's shape as much as possible.
Traditionally, implants, back muscles, and abdominal muscles were used for immediate reconstruction surgery. However, some hospitals are now performing reconstruction using the greater omentum, a type of intra-abdominal fat. Omental flap reconstruction uses a laparoscopic approach, minimizing scarring, providing a natural shape and feel, and promoting faster recovery.
After surgery and treatment, regular follow-up examinations are necessary. It is crucial to promptly inform your doctor of any unusual symptoms.
For instance, seek immediate medical attention if you notice lumps near the surgical site, under the skin, in the armpit, or above or below the collarbone; experience persistent weight loss, headaches, dizziness, shortness of breath, chest pain, coughing, localized pain, vision or sensory abnormalities, or seizures.
To prevent recurrence, maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is important. Unverified diets or alternative therapies should be avoided as they can interfere with treatment and recovery.
Many breast cancer patients experience depression or anxiety after treatment. It is important to maintain a positive attitude and confidence in overcoming the illness and returning to daily life. Consulting with your doctor or a professional counselor, and participating in breast cancer patient support groups can also be very helpful.
More helpful content from Bundang Seoul National University Hospital
View other posts



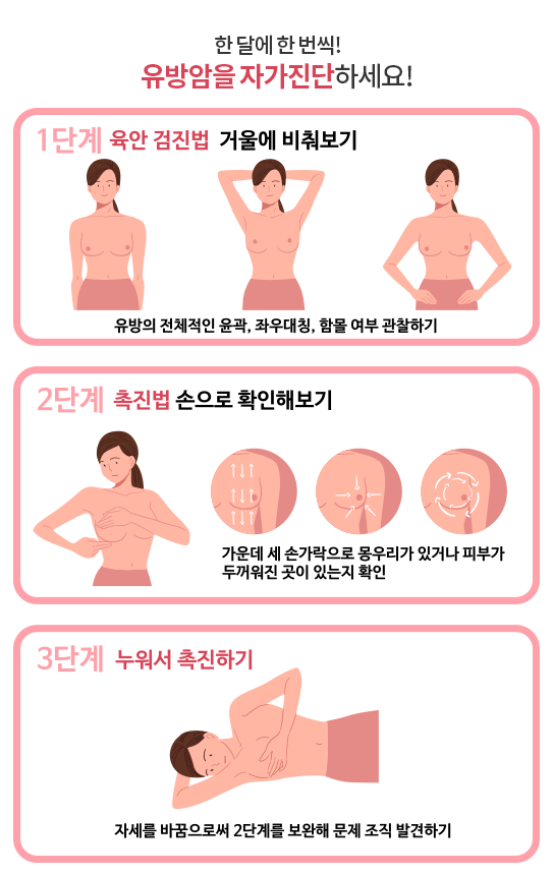



Source :https://blog.naver.com/happy_snubh/224019018627
- 이전글 Pre-Surgery MRI Reduces Breast Cancer Recurrence in Younger Women
- 다음글 Three Key Points for Early Breast Cancer Detection
댓글목록 0
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.
